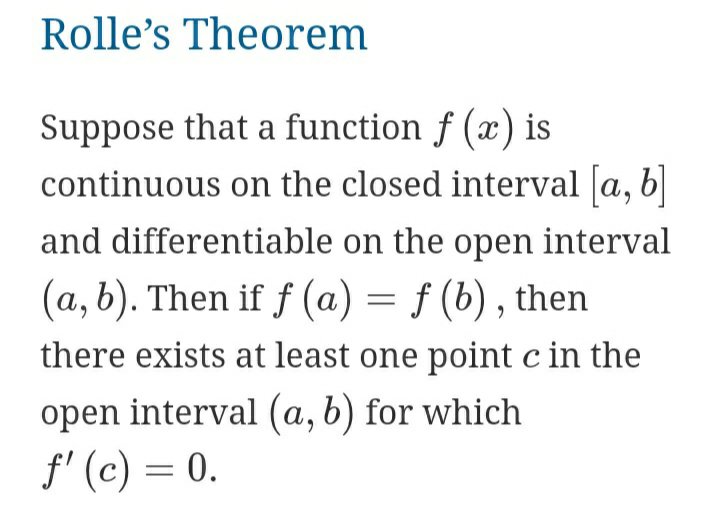
Rolle’s theorem, in analysis, special case of the mean-value theorem of differential calculus.
In calculus, Rolle’s theorem or Rolle’s lemma essentially states that any real-valued differentiable function that attains equal values at two distinct points must have at least one stationary point somewhere between them—that is, a point where the first derivative is zero. The theorem is named after Michel Rolle.